What Is Generative AI: A Deep Dive into the Latest Buzzword
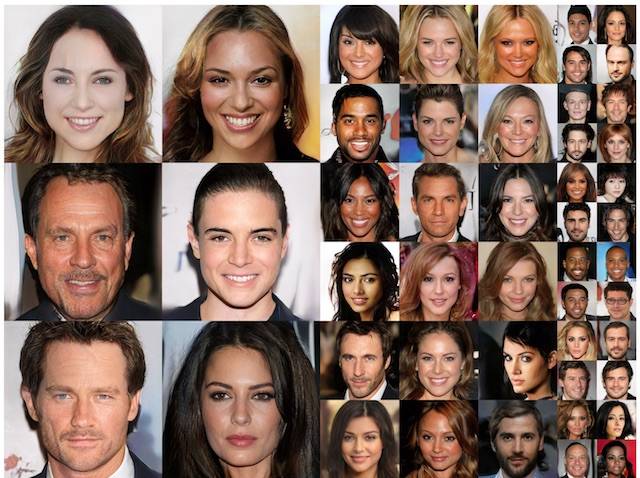
Gartner listed generative AI as among the 5 impactful technology trends for 2022. But before we get into the ins and outs of generative AI, we want you to have a look at the image below.
“But what’s special about these photographs?” you might ask. These look like a bunch of random people.
Well, technically yes and no. See, what makes this image special is that –
a) the photographs shown here are of people who don’t exist in real life
b) these realistic photographs have been created by an AI
This is the crux of what generative AI is capable of doing. Generative AI leverages machine learning and AI algorithms to create artificial content like images, text, audio, video, etc.
The images we showed above have also been created using generative AI where the AI model was trained using photographs of celebrities. That’s why these faces have some features similar to celebrity faces.
After ‘DeepFake’, ‘Generative AI’ is the latest buzzword in the tech sphere. It’s an evolution of AI that can create new content by utilizing existing content.
In this article, we’ll discuss what generative AI is, how it works, its benefits, use cases, and challenges. So, let’s get started.
Generative AI - Introduction
Generative AI refers to AI techniques that can read data (in the form of text, image, audio, video) and use it to generate brand-new and original content that preserves a likeness to original data.
As discussed above, generative AI can use unsupervised learning algorithms to create new plausible content using existing content. In other words, it allows machines to understand the patterns in the input content and use these to generate similar content.
Generative AI models are offered only limited parameters to use during the training. Due to this approach, the model draws its own conclusions about the data’s most important characteristics.
Hence, the results generative AI creates are without the biases of human experiences and thought processes. Until recently, most AI learning models have been discriminatory. However, generative AI can create synthetic data capable of passing the Turing test.
Moreover, generative AI requires more processing power and is, therefore, more expensive to implement.Gartner also predicts that by 2025, generative AI will account for 10% of all data produced.
Generative AI - Techniques involved
Generative AI uses the following techniques –
• Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are algorithmic architectures that use two neural networks and pit them against each other to generate new, synthetic data.
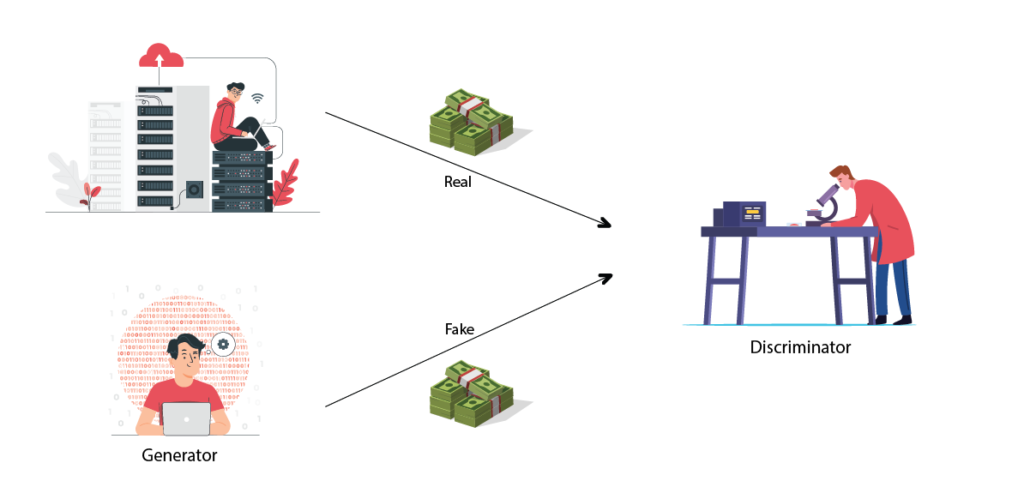
The two neural networks are called Generator and Discriminator. These two compete with each other to capture, scrutinize, and replicate any variations within a dataset.
The generator handles generating new data or content that resembles training data. The discriminator differentiates between the training data and generated data to recognize which one is close to the original data.
The image below showcases how GAN works. The database has real currency. The generator generates fake currency. The discriminator identifies real and fake notes.
• Transformers
Transformers are models like GPT-3 that are capable of imitating cognitive attention and differentially measuring the significance of the input data parts.
Transformers can understand language, images, or videos, and can learn some classification tasks to generate content from massive datasets.
• Variational auto-encoders
The encoder encodes the input data into a compressed code while the decoder uses this code to reproduce the initial information.
When properly trained, this compressed representation stores the input data in a much smaller dimensional representation.
Benefits offered by generative AI
Among a number of key benefits that generative AI can offer businesses, here are the key ones –
- Generative AI enables the creation of advanced, higher-quality outputs by unsupervised self-learning.
- It decreases the risk associated with a new design.
- The output produced by generative AI is not biased.
- It can provide deep predictions without using any sensors or detectors.
- It can empower AI bots to use maximum concepts in real and virtual worlds.
- It has a better understanding of abstract concepts.
Key use cases of generative AI
Among a number of key benefits that generative AI can offer businesses, here are the key ones –
- Generative AI has major applications in identity protection since generative AI avatars can provide protection to people who may not want to disclose their identities. For example, generative AI has been used to protect the identity of interviewees in news reports.
- Generative AI can be of great help in image processing. It can be used to intelligently upscale low-resolution images to high-resolution ones.
- Similar to image processing, generative AI can also be used in film restoration where it can enhance old movies by upscaling them to 4K resolution and beyond. It can remove noise, add colors, or make the video sharper.
- It has applications in audio synthesis where organizations can use it to generate a computer voice that sounds like a human voice. This can be used for narrating videos, movies, etc.
- In healthcare, generative AI can be used to render prosthetic limbs or organic molecules from scratch using 3D printing. Big names like IBM are using generative AI to research antimicrobial peptide (AMP) to find drugs for Covid-19. It also enables early detection of certain conditions to effective treatment options. For example, GANs can compute different angles of an x-ray image to visualize possible tumor expansion.
- Generative AI can help the reinforcement machine learning models to be less biased. It can comprehend more abstract concepts and thus has applications in robotics control.
- AI is already being used in sentiment analysis but using generative AI can improve it further.
- It can be used in automated fraud analysis where it can detect illicit transactions using predefined algorithms.
- Generative AI can benefit the design industry too to support designers.
- In the software industry, generative AI can automate manual coding work. So, instead of coding the entirety of the software, it can develop a solution by giving AI the context of what they need.

Challenges associated with generative AI
Despite all that it has to offer, generative AI has its own set of limitations. Let’s discuss some of the most prominent ones –
- Some GANs models are unstable and can be hard to control at times. They sometimes generate unexpected outputs, without a feasible explanation.
- Although generative AI can create new content, it cannot create entirely new things. It can only combine the data it has been fed in new ways. Moreover, a vast amount of training data is required to train generative AI.
- Generative AI can also be used by malicious actors for deceitful purposes like fraudulent activities, scamming people, fake news, etc.
- Some health-related applications may have privacy concerns.
Conclusion
Generative AI is in its nascent stage right now, with applications in limited industries. But it’s bound to disrupt a lot of other industry verticals. In the coming years, we are likely to see a much broader range of use cases as different sectors adopt this technology.
Did you enjoy this piece? Check out Dresma’s blogs to find more such insightful articles.


